Resources
The Resources section of the hosting Control Panel provides detailed information about your web hosting account resources usage. You can check detailed statistics on your disk space and traffic usage, CPU/MySQL usage, as well as monitor the currently running processes on the account.
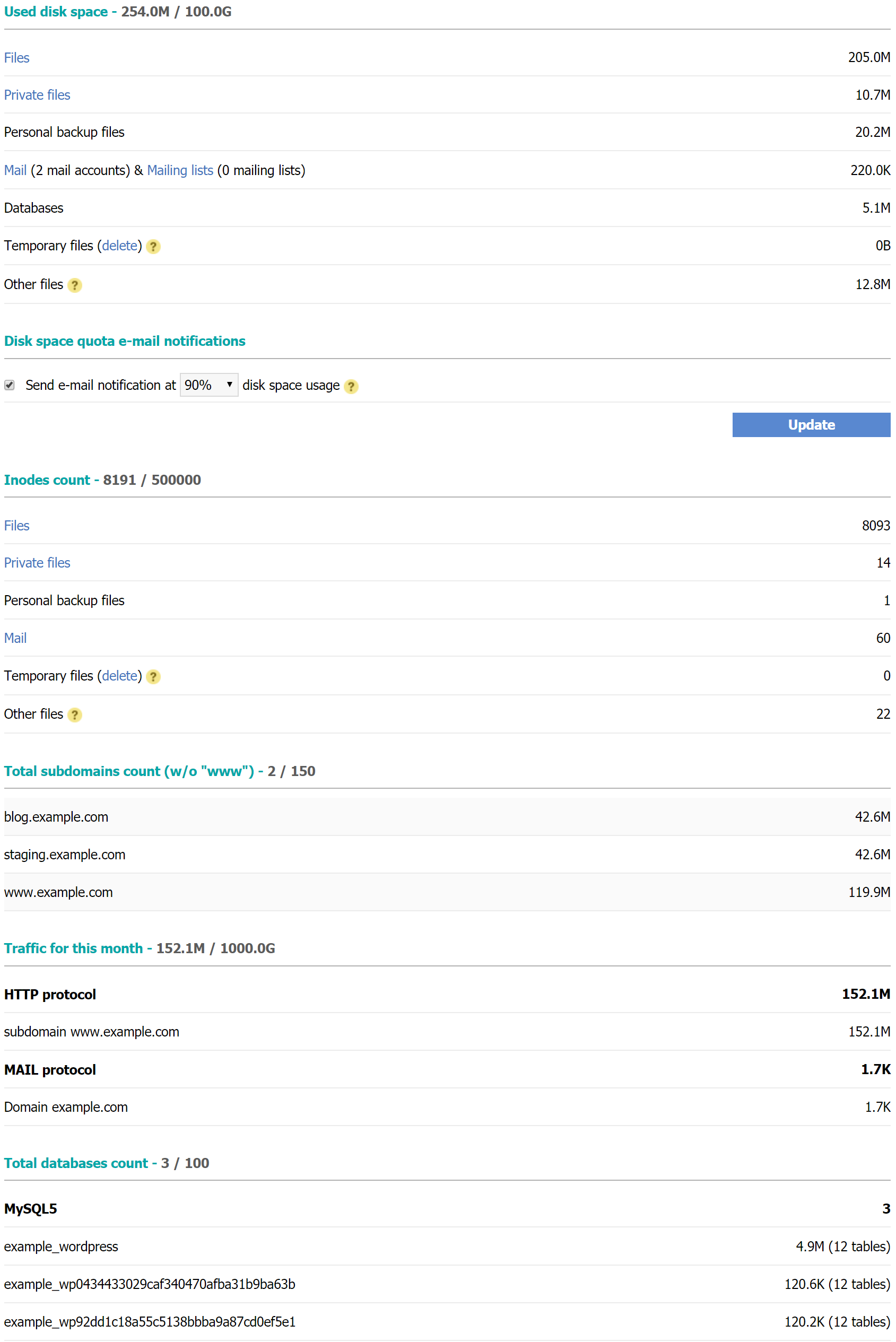
E-mail notification on disk space usage
If your account reaches its quota limit, some functions may stop operating properly. For example, you will not be able to receive new email messages. Also, some server side applications such as PHP/Perl/Python scripts require free disk space to write temporary files. If the account has no free space, such scripts may stop working properly. That is why it is strongly recommended that there is always some free space on the account.
When the account reaches 99% of its allowed quota, we will send a notification to the contact email address listed under the Account Profile section of the Control Panel. Also, the option "Send email notification at XX % disk space usage" allows you to set one more notification to the same email address at a custom level desired by you. This option is enabled by default for new accounts at 90% disk space usage. It is generally recommended that you leave it enabled as to know earlier that the account is near its disk space quota and take the appropriate measures to free space on the account.
Inodes count
There is a limit on the number of inodes you can have under your hosting account. You can see the number of inodes you currently have at this section. Your files, directories, mail messages, and symlinks are all inodes. If you have reached or are close to reaching your disk space quota, you can check our Disk space/inode quota reached article for general information on how to investigate and resolve the problem.
 | Notice on mailboxes disk space usage: |
In some cases, the mailboxes disk space usage displayed in this section may differ from the data displayed at the Mail Manager section of the hosting Control Panel. This is because the Resources section displays the disk space usage as it is on the server hard disk and is reported by the file system, while the Mail Manager section displays the information provided by the mail server software. The difference may come from:
- Messages in Trash which are counted as a hard disk space in the Resources section, but are not counted towards your Mail Manager quota.
- File compression for copied messages. Only the first message copy uses server hard disk space, but all copies are counted towards your Mail Manager quota.
- The block size of the file system and file metadata. If you have a large amount of very small email messages, the size on the hard disk may be larger than what is reported by the mail server software in the Mail Manager section.
It is important to know that a mailbox will be considered full and will bounce email when it reaches 100% of its allowed usage calculated by the Mail Manager, or when the hard disk quota of the whole hosting account is reached.
Note: The files in the ~/awstats, ~/logs, and ~/stats directories are not counted toward the account's disk space usage.
CPU and MySQL time tab
This tab displays the CPU and MySQL usage of the account for the last several weeks, as well as the hourly CPU usage for the last couple of days. If the account is close or over the allowed limit, the usage will also be displayed on the left pane of the hosting Control Panel.
- CPU time, daily usage - This histogram shows how much CPU time was used each day for processing instructions for your account. The data you see here shows the total daily CPU usage of all scripts running under your hosting account.
- CPU time, hourly usage - This histogram shows the hourly CPU usage of the account for the last 50 hours.
- MySQL time, daily usage - The MySQL time histogram shows details about the MySQL load generated by queries executed by your account. The figure displayed here is a sum of the CPU minutes needed by the MySQL server to run your queries and the I/O generated by the same queries.
The resources indicators on the CPU and MySQL usage do not represent hard limits on our end. Reaching the displayed limit does not mean that you will have a service suspended, but means that you need to take measures to optimize your software/scripts. We will not impose hard limits on your account as long as there are enough resources on the shared server. However, the stability of the servers is always our priority, and we cannot allow a single account to endanger the server performance.
The optimization of your software may include (but is not limited to):
- Updating all software to the latest stable versions. This is valid especially for popular software packages, including their themes and plugins.
- Checking if you have any plug-ins/add-ons installed to the software, and disabling any you do not really need. A badly written plug-in can seriously slow down your site's performance.
- Checking for any caching options/add-ons for the software you are using. They should significantly improve the performance of the application.
- Revising your MySQL queries, and making them more efficient. Having proper indexes for your tables will improve the efficiency of your MySQL usage.
- If you are using your own scripts, revising your code, and optimizing it.
- Converting your software to use static content (not dynamically generated by server-side scripts) whenever possible.
- Seeking professional help on service/software optimization.
Processes tab
The Processes tab shows the currently running processes on the server for your account. This section also allows you to kill stalled processes. There are several types of processes displayed:
- User processes - processes started by the scripts on your hosting account. Static pages (HTML) do not generate user processes.
- System processes - these processes are vital for the operation of your account and cannot be killed through this section.
- FPM processes - processes used by the system to serve requests for PHP scripts using the FPM with OPcache handler. They can be killed by reloading the FPM master process.
- FTP processes - these are started by FTP transfers to and from your hosting account.
- SSH processes - processes started by SSH sessions to the server.
- Web apps processes - these are processes used by the WebApps section of the Control Panel.
As a stability precaution, the number of simultaneous processes each hosting account can run is limited. This is valid for all types of processes.
If your site starts displaying an error "Unable to start another process", this means that its simultaneous processes limit is reached. This could be due to a problem with the site software itself, a connectivity issue from some visitors to the server, an attack against the site, or simply due to too heavy usage. In this case, you can use the current section to see if there are stalled processes and kill them.
The FTP processes limit could be reached if a single user/IP is creating too many connections to the server. Again, this could be due to a connectivity issue from the user to the server, or due to a problem with the FTP program used. Most FTP programs allow you to limit the number of simultaneous connections to the server, and it is advisable to set this limit to 2-3 connections.